A type of natural growth media-rich in nutrients, extracted from cattle meatpacking; as a byproduct is known as fetal bovine serum.
Tissue culture or cell culture is one of the most valuable, important and advantageous methods for the plant, animal and bacterial culture. Culture or cell culture is an artificial method to grow cells outside their natural system or in a lab.
To do so, researchers need artificial, aseptic and nutrient-rich sources of energy that help cells to proliferate. A wide range of artificial and natural media are now commercially available.
Note that the source of nutrients is known as “media” or “medium” in standard tissue culture techniques. Three basic ingredients are needed to grow a cell either in vivo or in vitro– Nutrients, proteins and energy.
Two common media types used commonly are serum-free media and serum-containing media. If you wish to learn more about serum-free and serum-containing media, you can read this section of our previous article: article.
The fetal bovine serum is a type of media that contains serum. In the present article, we will understand the basic concept of fetal bovine serum, its applications and why it is used in tissue culture.
What is FBS- Fetal Bovine Serum?
The basal supplement media is incomplete without serum which provides vital nutrients for cell division. FBS is one of the common serums used, however, which serum to use in cell culture depends on the chemical composition of basal media, the type of cell to be grown, culture system and purpose of the experiment.
The Fetal Bovine Serum abbreviated as FBS is a common natural media for cell culture or tissue culture rich in nutrients. Theodore Puck first used FBS for cell growth in 1950.
The FBS is widely applicable in biotechnology, biology and pharmaceutical research and diagnosis of disease. It contains a higher amount of albumin required for cell proliferation, especially for eukaryotic cells.
The FBS is derived as a byproduct of the meat industry, nonetheless, it is very important to process and purify it before using. It is a type of natural media, researchers modify and use as per their requirements.
Research, academics and diagnostic industries need FBS exclusively in almost all tissue culture experiments. Put simply, it’s a fluid or liquid derived from blood after blood clotting. Once blood clotted, a fluid that remains on the top is our FBS.
Noteworthy, we can’t produce and process FBS without prior government permission as there are ethical issues associated with it.
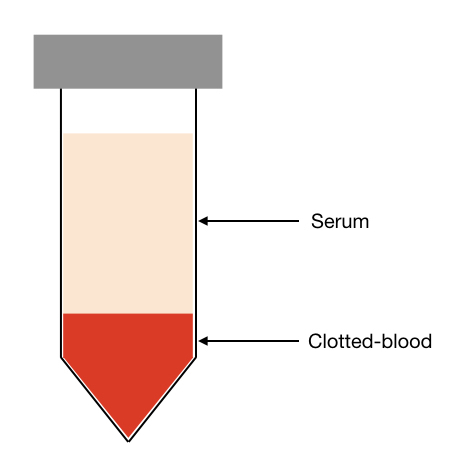
Meaning of Fetal Bovine serum:
Fetal- fetus or related to embryo; Bovine- Cow and serum- cell-free fluid.
A cell fluid derived through a standard scientific process from the fetus or embryo of a Bovine or cow is known as fetal bovine serum or FBS. To understand the concept of FBS more in-depth one should understand the differences between bovine serum and fetal bovine serum.
Bovine vs Fetal bovine serum:
First, understand that both are the type of serum and derived from cow or calf or bovines. However, the bovine serum is derived from the adult calf or newborn bovine while the FBS is only derived from the fetal bovines.
The FBS adds more value and hence employed commonly than any other bovine serums as it is richer in nutrients.
FBS gives excellent results in comparison to other bovine serums.
On the downside, ethical issues are involved in isolating, processing and distributing FBS.
Why is only fetal bovine serum used?
There are numerous options besides FBS, such as horse, goat and rabbit sera available to grow cells however, the most trusted one is the FBS. There are many benefits of it.
- First, the FBS or fetal bovine serum is widely used and proven serum media for eukaryotic cell culture.
- It contains more nutrients than any other sera or bovine serum.
- Also, it has fewer protein components that hinder cell growth.
- It contains less gamma globulin and more fetal albumin than other natural media.
- It has fewer antibodies, especially IgG which binds to cells preliminary to stop cell growth.
- Less complement protein in FBS also minimizes undesirable side effects.
The above-enlisted benefits make it more effective and useful than other serum and sera.
Related article: Explaining the whole karyotyping technique and procedure.
Benefits of FBS:
- Rich in nutrients- filled with cell proliferative components.
- Provides buffering capacity.
- Neutralizes toxins.
- Supply energy, carbohydrates and protein to the culture
- Provides vitamins, trace elements, transport proteins and other protein factors which are necessary.
- Also provides adherence and extension to culture.
- Provides hormones for better growth.
- Facilitates a better environment for excellent in vitro cell culture.
- Also, stabilize the culture and minimize toxin effects.
- Induce cell differentiation.
Production and processing of FBS:
The whole process of serum preparation is divided into four steps: Production, processing, testing and storing.
Cattle blood, a byproduct of slaughterhouses, is used to prepare the FBS.
A method, known as a cardiac puncture in which blood is drained directly from the heart of slaughtered cattle fetuses.
The procedure is performed aseptically to minimize the risk of contamination and blood is collected in sterile plastic bags to clot.
After collection, the blood is allowed to make free the serum component followed by centrifugation.
Centrifugation enables the separation of two phases from which the serum is collected. The collected serum is sent for filtration to remove other contaminants.
Usually, bacteria and fungus are removed using a sterile 0.1-micrometer membrane filter, however, viruses can’t. Note that to make it more effective, the filtration is performed thrice.
Irradiation by gamma rays helps to remove viral contaminants.
The raw serum is stored below 10°C temperature for longer use.
In the next phase, different testing is performed in order to validate the lot of serum which are screening tests for virus and mycoplasma, microbial sterility testing, endotoxin, hemoglobin and IgG testing.
Total protein assay and fibrin assay are also performed prior to distribution and use. Common test are enlisted here in the table:
| Test for FBS |
| pH test |
| Osmolarity |
| Sterility testing- bacterial and fungi |
| Endotoxin |
| Hemoglobin |
| Immunoglobulin testing |
| Bovine virus diarrhea |
| Cytopathic agents |
| Performance testing |
| Protein assay |
| Fibrin assay |
| Radial diffusion assay |
FBS- storing and testing:
FBS itself is a sensitive fluid and used in sensitive experiments such as cell culture and so to maintain its integrity and to improve productivity, it is stored frozen usually between -5°C to -20°C.
Note that some serum can’t be frozen, that is a different thing!
To use it, thaw FBS aseptically between 2°C to 8°C temperature. At higher temperatures the chances of contamination and degradation of FBS elevates. Note that sometimes, crystals or precipitates are observed after thawing due to protein portion. Precipitates can be removed by centrifugation.
It is advisable to store FBS in different aliquots as per the requirement.
Production, processing, testing and distributing FBS is strictly regulated by international and national authorities. Multifaceted ethical issues are involved in the whole process consequently safety guidelines and quality testing is compulsory.
Note: 2 to 10% serum is added in the culture depending upon the assay to improve cell proliferation.
Read more: What is Karyotyping?- Definition, Steps, Process, and Advantages.
Things should be present!- nutrients, embryonic growth factors, carrier proteins, macro proteins, hormones and vitamins.
Things should not be present!- endotoxins, hemoglobins, fibrins, immunoglobulins (antibodies) growth-inhibitory components and other toxins.
Component of complete media:
| Component | Concentration (V/V) |
| MEM (medium) | 87% |
| Antibiotics | 1% |
| Fetal bovine serum | 10% |
| Amino acids | 2% |
| Total | 100% |
Testing of FBS:
To ensure the quality of the FBS or any other serum, there are several test must be performed before use or distribution, those are divided into four broader categories; Microbial testing, Biochemical testing, Physical & chemical testing and Performance testing.
Here we have enlisted list of test in each category:
| Test | Specification |
| Microbial testing | Sterility tests: Bacteria and fungus Mycoplasma contamination testingEndotoxin testingViral testing using irradiation using gamma raysViral antibody screening |
| Biochemical tests | Test for cholesterol, creatinine, creatine kinase, Bilirubin (Total and direct), aspartate, lactate, glucose, HDL, LDL, Blood urea and nitrogen, Alanine, ALT- transaminase, alkaline phosphatase, chloride, calcium, triglycerides and Uric acid. |
| Physical and chemical conditions | pH, osmolarity, IgG and immunoglobulin testing, Globulin, Hemoglobin, Electrophoretic pattern, Protein electrophoresis |
| Performance testing | Cell proliferation efficiency testing Testing for culturing abilities on varied cell lines. |
Companies and researchers prefer to use the USA- FDA approved FBS only. However, different kinds of FBS options are also available for different cell cultures. Some of them are Direct filtered FBS, Heat inactivated FBS, Charcoal treated FBS, Gamma irradiated FBS and Dialyzed FBS.
Filtered FBS:
This FBS is widely used, filtered using the 0.1micron sterile filter paper trice. The filtration removes bacteria and fungus from the FBS if any. Filtered FBS usually gives excellent results if approved by the FDA.
Charcoal treated FBS:
Hormones such as testosterone, cortisol, andronen, estradiol and other steroids hinder in cell differentiation in some cell lines. To use the FBS effectively for those cell lines, hormones must be removed from the FBS before use, if any.
The active charcoal carbons bind to the lipophilic end of hormones and remove it by washing. Note that dextrans is also applicable to remove hormones from FBS.
Heat inactivated FBS:
Some growth inhibitors still remain active even after filtrations and centrifugation which abrupt cell proliferation. Simply, heating the FBS before using, can inactivate those inhibitors.
To do so, the FBS is placed in the 60C water bath for 30 to 40 minutes, however, heating also deactivates other growth promoting factors and leads to precipitation of important proteins.
Heat inactivation is usually not advisable.
Dialyzed FBS:
Also known as diafiltration removes some of the ingredients which aren’t needed in the culture such as amino acids, antibiotics and hormones under the molecular weight of 10,000.
The process is performed in order to maintain the proliferative capacity of the serum. In the process, the FBS is circulated aseptically in the hollow-fibers.
Note that confirmatory testing is required to validate FBS dialysis.
Gamma irradiated FBS:
Filtration or dialysis can’t inactivate viruses as those are tinier. Gamma irradiation is a process to deactivate viruses in order to improve the quality of FBS.
Cobalt 60 is the radioisotope that emits gamma rays that breaks the nucleic acid bonds and inactivates viral particles. Noteworthy, gamma irradiation can’t alter the properties of FBS at all.
Along with alliteration, gamma irradiation is commonly employed to assure good quality of fetal bovine serum. Scientists across the world prefer gamma irradiated FBS.
Regulating FBS or serum biowaste:
This section is very important for researchers and newbie scientists- managing the biowaste of FBS. FBS or any serum is used to grow cells we wish to study, however, lack of a sterile environment causes growth of many other microbes as well.
Even if we let it put in normal conditions for some days, many specified and unspecified microbes are grown in it. Therefore if the FBS waste is treated like a normal waste, it is dangerous.
Suppose if a bottle uncapped or vial of FBS is thrown outside the lab, many unwanted microbes will grow in that contaminant environment, surrounding and lab as well. Some microbes are lethal as well.
Thus it is important to manage the FBS or serum waste properly. In order to dispose of FBS, unused FBS or leftover FBS, first make it heat inactive by boiling and discard in an air tight bottle.
Consider it as biowaste and discard accordingly.
Don’t drain it in the sink or basin.
Applications of FBS:
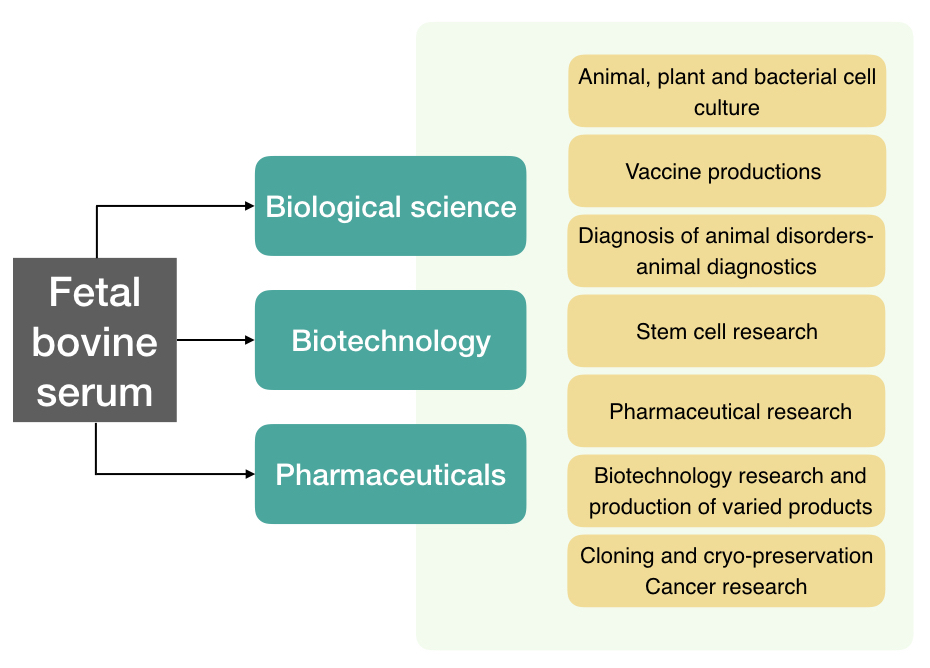
Animal, plant and bacterial cell culture
Cell culture is one of the best methods to study and investigate organisms and their properties. This needs nutrients and contamination free areas. The FBS- fetal bovine serum is one of the main ingredients of the basal nutrient media. However, FBS free media are also available notably.
Vaccine productions
Vaccines are the heat-killed or inactive viral particles employed to protect our body against viruses. To do so, the FBS is used in the culture media as an ingredient to grow transformed bacterial cells.
Diagnosis of animal disorders- animal diagnostics
To culturing cells the anatomy, physiology and structure of a cell can be studied. Cell investigation helps to understand how cells behave in different disease or non-disease conditions.
Animal cells can be cultured using the FBS containing media, allowing them to proliferate and investigate.
Stem cell research
One of the best applications of the FBS rich media is in the proliferation of stem cell lines or other proliferative cell lines. This allows scientists to study and prevent various disorders such as cancer, thalassemia or other disorders.
Isolated cell cells are cultured under aseptic conditions using the basal media with or without serum (FBS). FBS containing cell media are highly recommended.
Pharmaceutical research
FBS and related media or basal media are also employed in pharmaceutical research. The effect of different drugs and medicines can directly be studied on cell lines by growing cells through basal, FBS-rich culture media.
Biotechnology research and production of varied products
One of the biggest applications of cell culture and FBS is in experiments and research in biotechnology industries. Effect of different therapies, gene-altered products, CRISPR-CAS9, gene-editing and other genome alteration experiments are only possible by culturing target cells.
FBS containing media are widely used in biotechnology cell culture experiments. Fetal bovine serum provides excellent stability, proliferation and nutrients.
Cloning and cryo-preservation
Preserving cells and culture media is as important as culturing cells. Freezing at lower temperature decreases the viability of cells and productivity of culture media.
To protect each, we need to cryo-preserve them precisely and effectively which is done using the FBS. The fetal bovine serum plays a major role in reducing oxidative stress and as well as preserving culture media.
With the combination of DMSO, FBS as a cry-preservator functions excellently.
In addition, cloned cells are also cultured using the FBS rich media.
Cancer research:
Yet another crucial application of the FBS is in cancer research. As we said, the topology, anatomy, structure and behaviour of the cancerous cells can be studied by culturing them in vitro.
Read more: What is karyotyping used for?
Common tips to use, maintain and process FBS:
Here are some of the practical tips that help you to handle FBS correctly.
- Do a physical examination once the bottle reaches. A fresh and sterile FBS should have a clear yellowish color.
- It shouldn’t have precipitated in it.
- The Bottle must be capped properly.
- The bottle must be received in a proper temperature chain (under dry ice at -5°C to -20°C).
- The bottle must have correct certifications such as FDA, CE, ISO etc.
- Only a maximum of 10% FBS in the medium.
- Store and use in different aliquots to minimize the risk of contamination.
Limitations of FBS:
Though FBS has unmatched applications in biotechnology and biology, however, plenty of limitations it has.
FBS is one of the major sources of contamination in culture. There are huge chances of xeno-immunization and zoonotic transmission.
Batch to batch the efficiency varies greatly.
Ethical issues are involved in collecting blood from fetuses.
The entire process of production, processing and distributing FBS is regulated by government bodies.
The presence of endotoxins, hemoglobins and other proteins may also abrupt the growth of cells.
High end safety level and state-of-the-art laboratory set is required.
Here are some of best FBS options from ThermoFisher: Range of FBS from ThermoFisher.
Conclusion:
FBS- fetal bovine serum is an excellent nutrient source in animal cell culture and added to the basal culture media. Nonetheless, there are plenty of ready-to-use culture media that are nowadays available.
The FBS in culture used since long, though there are chances that the basal media got contaminated while adding the FBS.
I personally prefer to prepare the media using the FBS so that as a newbie you can understand the importance of the FBS and the criticality of experiments. Noteworthy, for crucial applications, scientists recommended ready-to-use media.